What is DHCP?
Every device connected to a network must be configured with an IP address in order to communicate. This can be done using a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), a network management protocol responsible for assigning and leasing new, dynamic IP addresses as well as propagating the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server to network devices as they connect on a LAN.
Through automatic and dynamic allocation, DHCP automates and centrally manages these configurations rather than requiring network administrators to manually assign IP Addresses to all network devices. It can be implemented on small local networks, as well as large enterprise networks.
DHCP in the Graphiant Portal
From within the Graphiant Portal, you will be able to establish and configure DHCP connections to and between various network Edges under your control.
Step 1: Locating DHCP in the Graphiant Portal
From the Home screen, navigate to the Edge Configuration screen by one of the following:
Locate the "Configurations" section within the “Quickstart” area of the screen; select 'Configure Edges'.
or
Click 'Configure' in the sidebar; select 'Devices'.
.png)
This will take you to the ‘Configuration’ page of the Graphiant Portal where you will be able to view all active, staged, and deactivated Edges. From here you will be able to select among the active Edges which Edge(s) you would like to be configured with DHCP.
On the righthand side, select and click ‘Configure’ in tandem with the Edge you wish to manage.
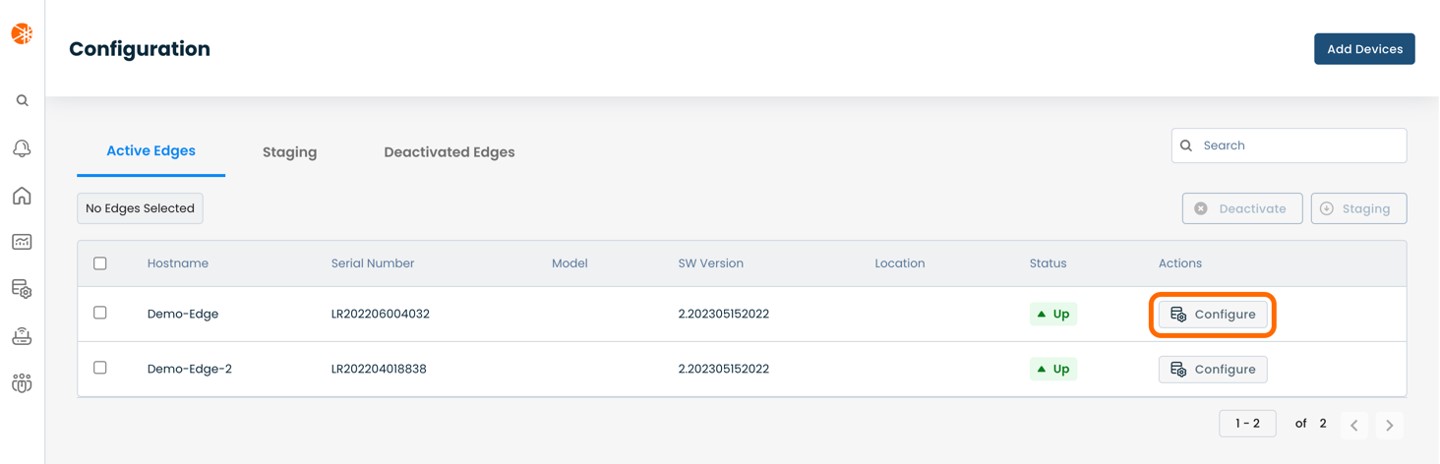
This will take you onto a Configuration page with a focus on the Edge you have just chosen.
Here you will see a list of headings along the lefthand side of the page, such as ‘Configure Network’, ‘Configure Services’, ‘Configure Policies’, etc.
From here, select and click ‘Configure Services’.
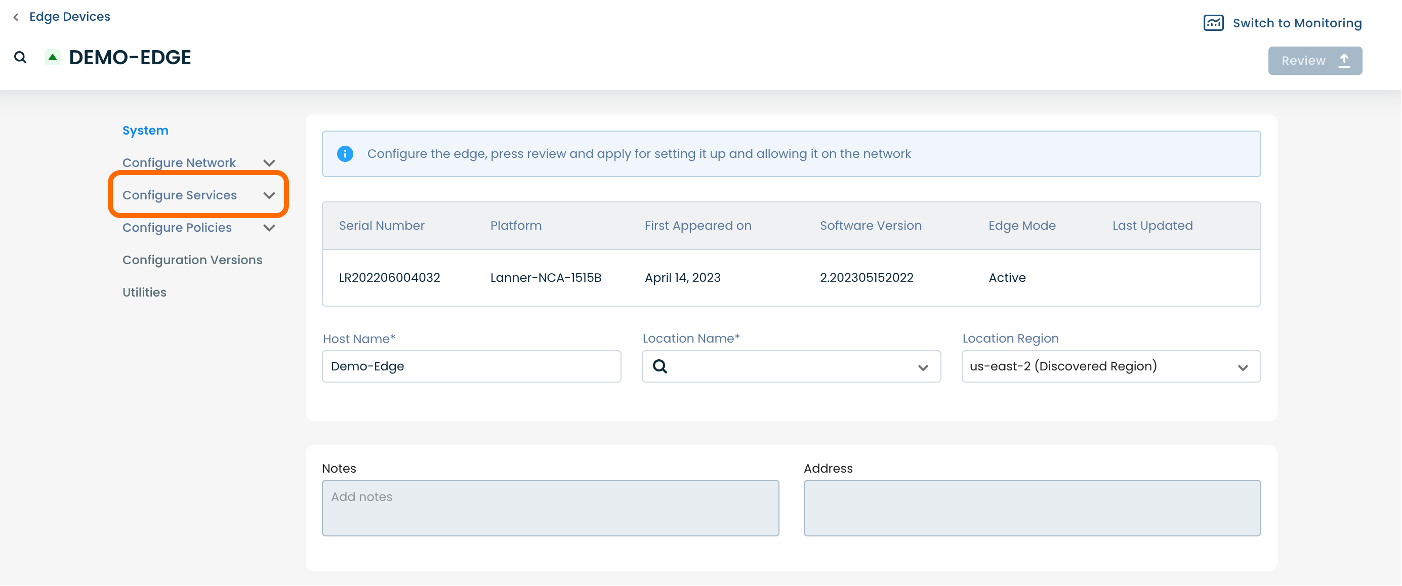
A dropdown menu will appear. From the dropdown menu, select and click ‘Edge Services’.
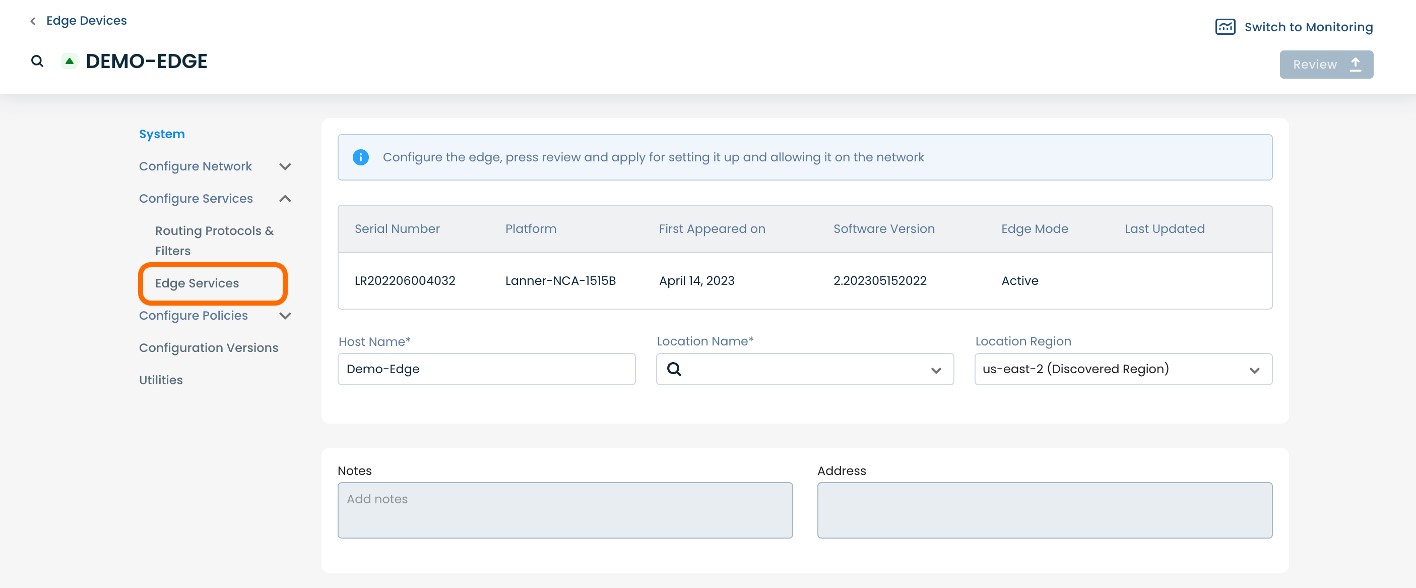
This will take you onto an Edge Services page dedicated to the chosen Edge.
On the Edge Services page, you will see a list of available headers along the top of the page such as ‘Firewall’, ‘Syslog’, ‘DHCP’, etc.
Select and click ‘DHCP’.
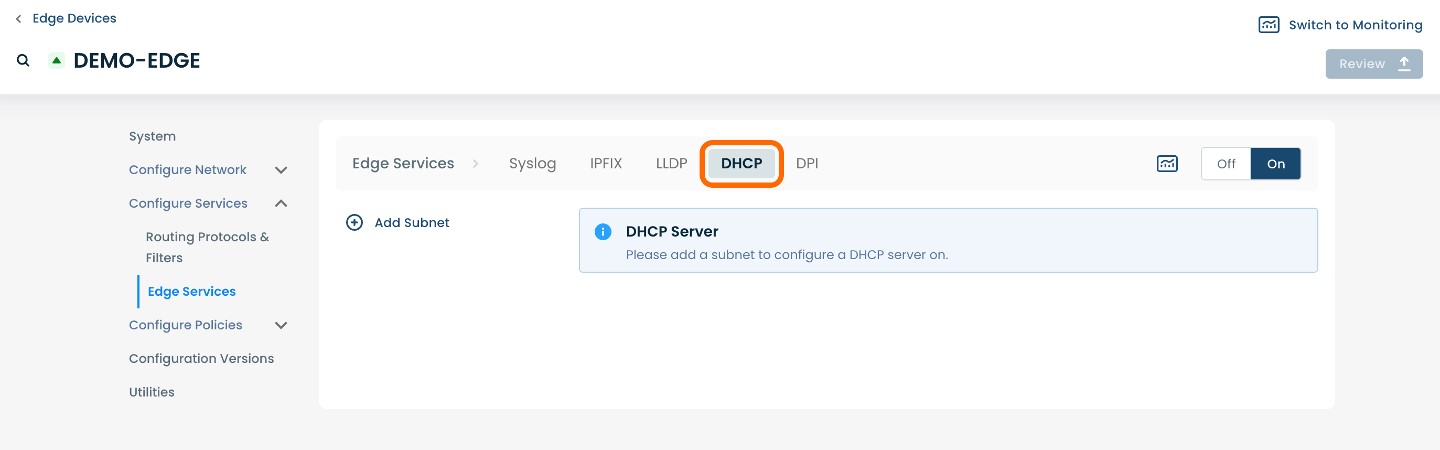
Step 2: Adding a Subnet in the Graphiant Portal
Now that you have located DHCP within the Graphiant Portal, it is time to establish a DHCP scope.
Note:
In this context, subnet is referring to “scope” and does not in fact create a subnetwork.
A DHCP scope is a valid range of IP addresses that are available for assignment or lease to client computers on a particular subnet. Users can configure as many scopes as required in the network environment.
In order to establish a DHCP scope, you will first need to add a subnet onto which you’ll configure the DHCP server.
To add a subnet, select and click ‘(+) Add Subnet’ at the center of the page.
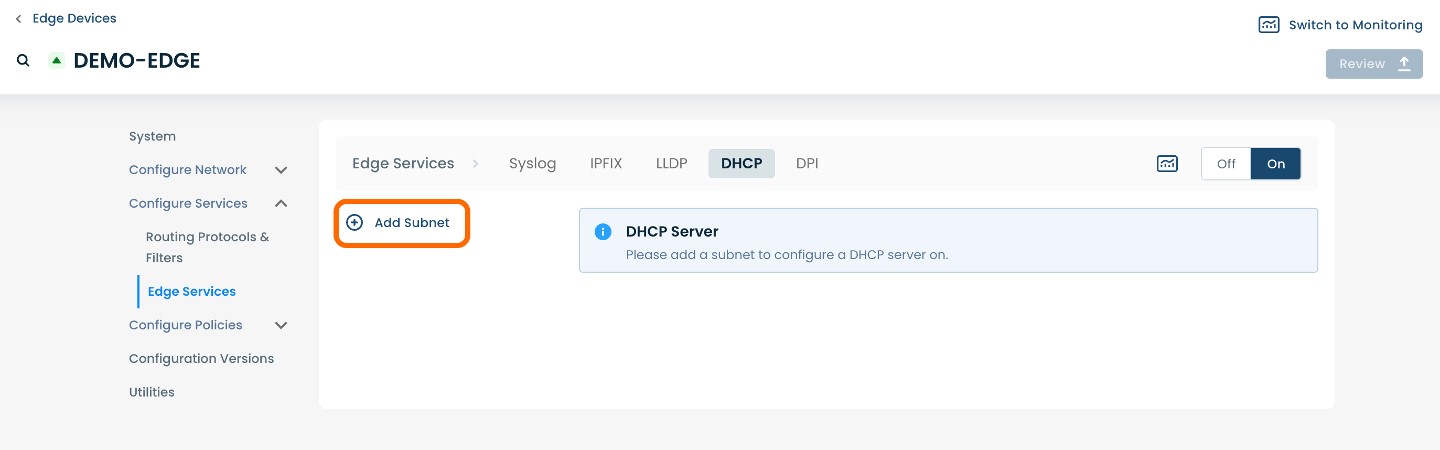
The page will propagate various fields of required information.
Step 3: Setting Up DHCP in the Graphiant Portal
Below are descriptors for each of the fields required in order to establish a DHCP server.
(An * indicates a required field.)
Choose Subnet Type: Choose either DHCPv4 or DHCPv6.
LAN Segment: Choose a desired LAN Segment from the pre-populated list based on previously configured LAN segments .
Interface*: Choose a desired Interface from pre-populated list based on interfaces assigned to the previously selected LAN segment.
Subnet Name*: Choose a name to label the subnet.
Description: Choose a description to label the subnet.
IP Prefix*: IP prefix that addresses will be assigned from; for example: 192.168.1.0/24
Gateway*: IP address for the gateway router; for example: 192.168.1.1
Domain: DNS domain for host that will be receiving addresses
DNS: Translates domain names into IP addresses; choose one: Custom, Google, OpenDNS, or Cloudflare
Primary: Pre-populated based on selected DNS
Secondary: Pre-populated based on selected DNS
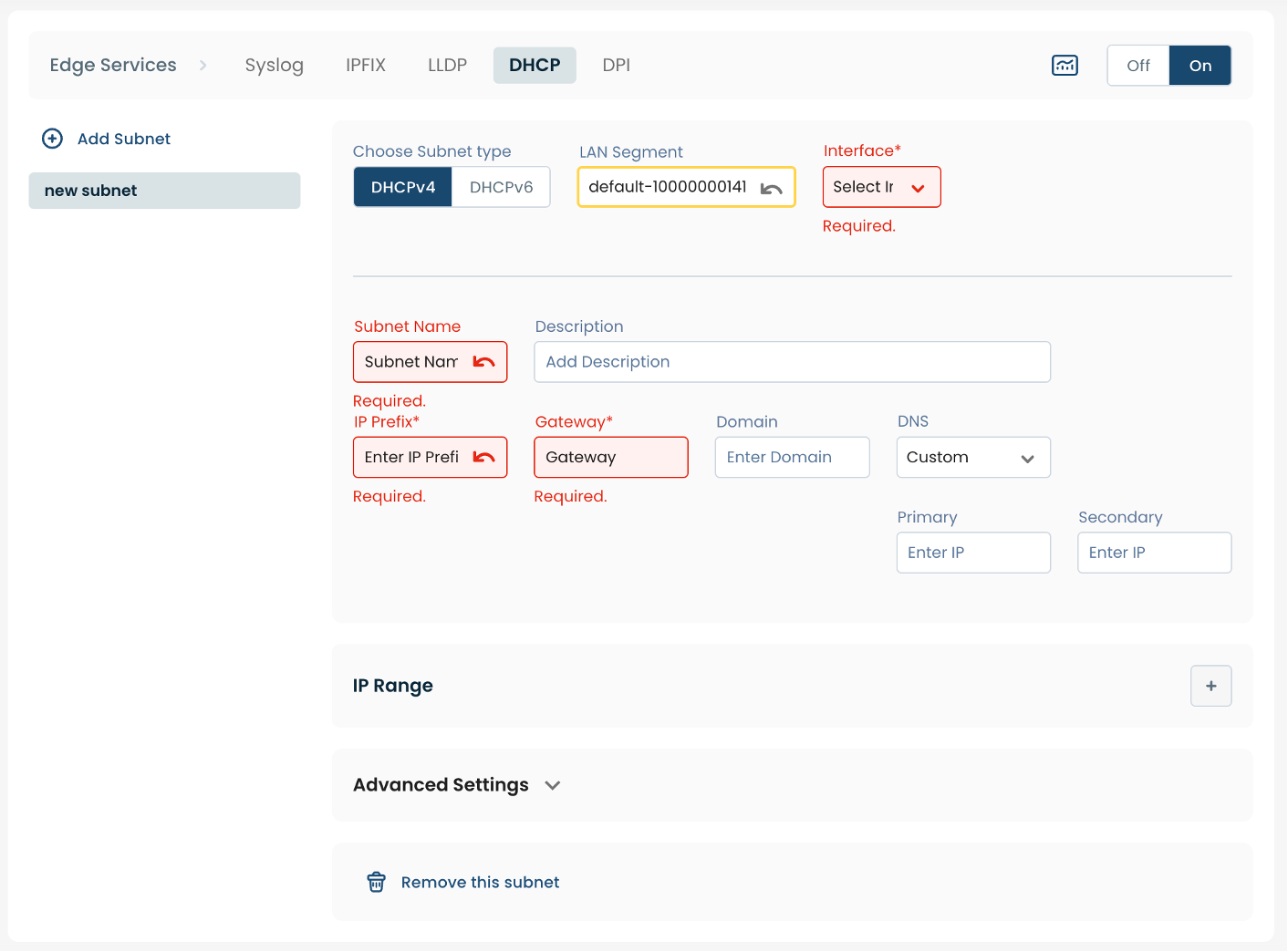
IP Range:
To enter IP Range, select and click (+) to the right of "IP Range".
Start: Starting IPv4 or IPv6 address for DHCP pool; for example: 192.168.1.2
End: Ending IPv4 or IPv6 address for DHCP pool; for example: 192.168.1.255
Note:
Be sure to make sure that the range of addresses you define matches up with the defined prefix/subnet for the interface for which you are configuring the DHCP server.
For example: 192.168.1.30 through 192.168.1.40
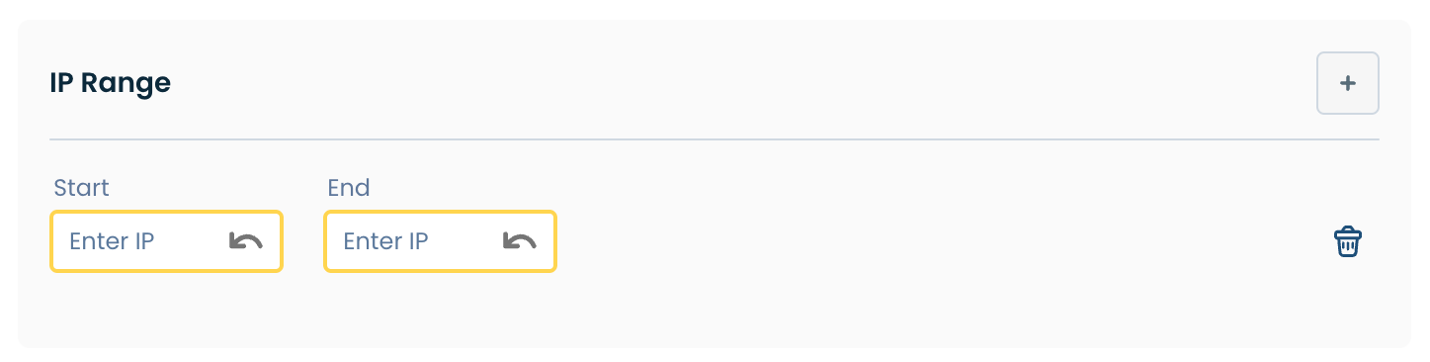
Advanced Settings:
Default: The length in seconds that will be assigned to a lease if the client requesting the lease does not ask for a specific expiration time; this is used for both DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 leases (it is also known as the "valid lifetime" in DHCPv6)
Max: The maximum length of lease time that will be supported in a client request
Min: The minimum length of lease time that will be supported in a client request
Step 4: Review & Apply
Once the above fields are filled in, the selected Edge device will be ready to begin functioning as a DHCP server, however you will first need to review and approve all changes made.

On the top righthand corner, choose from the following options:
‘Discard’ to discard changes made
‘Save as Draft’ to save changes made to be implemented at a later time
‘Review’ to review and apply changes made for immediate deployment
Note:
For connecting your devices to a DHCP server that is already established elsewhere on your WAN, please see Establishing DHCP Relay.